The Basics
- Operating profit margin is the ratio of operating income to net sales.
- Operating profit margin is similar to gross profit margin, another financial ratio, but takes it a step further by subtracting operating expenses in addition to cost of goods sold.
- Operating profit margin does not account for non-operating expenses like taxes and interest. It also doesn’t account for debt. Therefore, it’s not an accurate measure of business health on its own.
What is operating profit margin?
Operating profit margin, also known as operating margin or operating ratio, is a profitability ratio that represents the portion of total revenue that is left over after spending on the core operation of the business. It is usually expressed as a percentage. This ratio answers the question: For every dollar of sales, how much money does a business have left over after paying for materials and overhead?
Operating profit vs. operating profit margin
Operating profit is the same thing as operating income and EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Tax) margin. This is a dollar amount—not a ratio—that represents how much profit a company made during a period of time, after subtracting cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses. Operating profit (AKA operating income) is an input in the operating profit margin percentage.
How do you calculate operating profit margin?
Operating profit margin is the ratio of operating income to net sales. It’s calculated by a the following formula:
Operating profit margin = Operating income / Net sales
To convert the resulting number to a percentage, multiply it by 100.
Operating income and net sales (AKA, revenue) are both found on a company’s income statement.
- Operating income is a company’s total revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses. You can also calculate operating income by subtracting operational expenses from gross profit.
- Net sales is the company’s total revenue from sales minus returns and discounts.
Example of operating profit margin
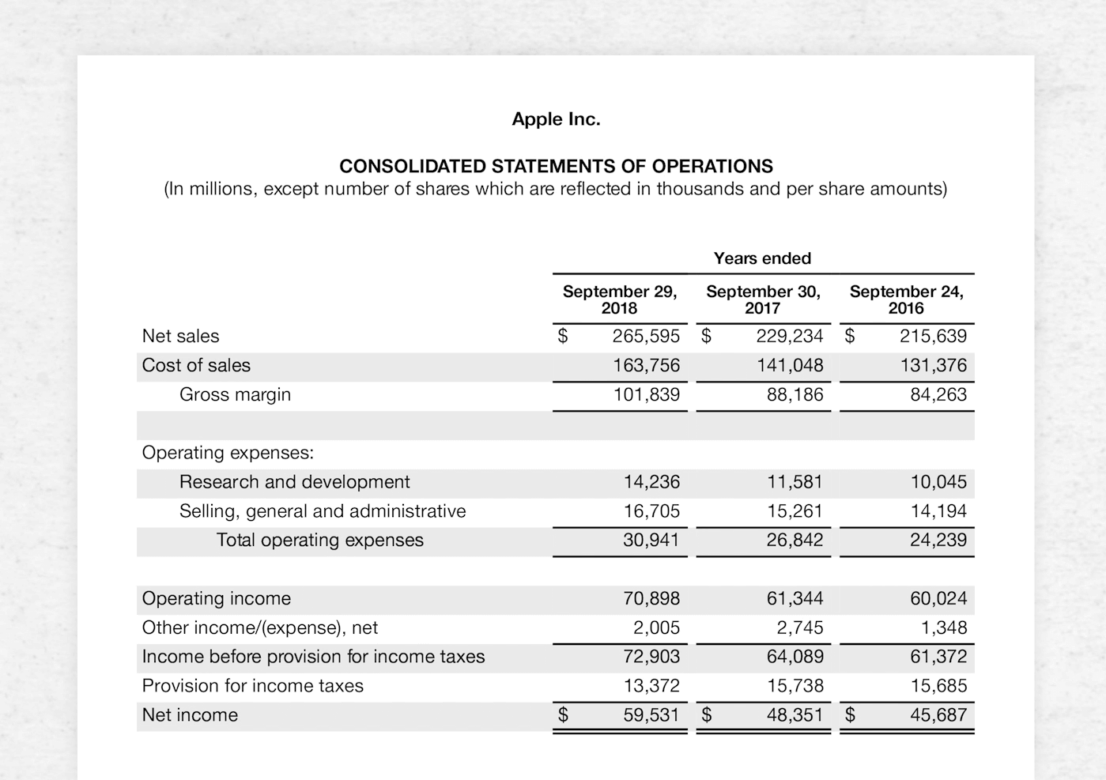
Consider Apple’s 2018 consolidated statement of operations. Apple reported the following totals (rounded for ease):
- Net sales of $265 billion
- Operating income of $71 billion
Operating profit margin = $71B / $265B
In this example, Apple’s operating profit margin was 0.268, or 26.8%
What does operating profit margin tell you about a business?
The operating margin ratio is a key indicator for how well a company can earn profits from its core product or service offering. Generally, the higher the ratio, the better a company is at turning sales into profits.
While this ratio is similar to the gross profit margin ratio in that both measure how profitable a company is, gross profit margin only subtracts costs associated with production and distribution, whereas operating profit margin subtracts operating costs as well.
Generally, you want to see operating profit margin increase over time, as that suggests that a company is becoming more efficient and retaining a higher percentage of every dollar of revenue.
Limitations of operating profit margin
- Operating profit margin is one measure of profitability, but it doesn’t give you a full picture of a business’s financial health.
- Operating profit margin does not account for non-operating expenses like taxes and interest.
- Operating profit margin does not account for debt.
Pareto Labs offers engaging on demand courses in business fundamentals. Built to help you elevate your game at work, our courses distill complex business topics — like how to read financial statements, how to manage people, or even how to value a business — into digestible lessons. No business background required. Our library of 200+ lessons will teach you exactly what you need to know to use it at work tomorrow. Sign up for a free trial today to start watching.

